Apple pie for maturing service industry in India
CONCEPT OF LLPs:
Limited Liability Partnerships can be defined as an alternative to the traditional partnerships and can most appropriately be described as a hybrid between a company and a partnership that not only provides the benefits of limited liability but allows its members the flexibility of organizing their internal structure as a partnership based on a mutual agreement arrived between them. Owing to flexibility in structure and operation, LLP are very much suitable for small enterprises and venture capitalists. Also it provides a platform to professional firms of Company Secretaries, Chartered Accountants, Advocates etc. to conduct their business/professional activities under the organisation structure recognised as separate legal entity, limiting their personal liability and increasing their global competitiveness.
INTERNATIONAL SCENARIO OF LLPs:
Internationally, LLPs are a very popular form of business but slightly vary from country to country. I .In United States , Limited partnerships emerged in the early 1990s; while only two states allowed LLPs in 1992, over forty had adopted LLP statutes by 1996, when LLPs were added to the Uniform Partnership Act (UPA) . Each individual state has its own law governing their formation. Although found in many business fields, the LLP is an especially popular form of organization among professionals, particularly lawyers, accountants and architects.
In the United Kingdom, The Limited Liability Partnership is a recent innovation of UK law, and has been introduced by the Limited Liability Partnerships Act 2000. The Act became law on 1st April 2001. In a LLP, all partners have limited liability, similar to that of the shareholders of a corporation. The partners have the right to manage the business directly and and they bind the firm by their actions. From the taxation perspective also LLPs are favourable since many countries have a different level of tax liability on partnership and LLP firms as compared to a corporation. Under UK law, the LLP is a “fiscal transparency, means that it is not subject to taxation and the only the members are liable to taxation.
 INTRODUCTION OF LLPs IN INDIA:
INTRODUCTION OF LLPs IN INDIA:
The unlimited liability of partners has so far been the primary reason for which Partnership Firm of professionals, have not grown in size to successfully meet the challenges posed by international competition,WTO,GATT etc. Much as an alternative to the traditional partnerships, Limited Liability Partnership structure was given a recognition through Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 . Limited Liability Partnership Bill, 2006 was introduced in Rajya Sabha on 15th December 2006 by Minister of Companies Affairs. The LLP Bill, 2006 introduced was broadly based on the UK and Singapore LLP Acts. The Bill was later referred to Department Related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance for examination and report. Keeping in view the recommendations made by the Standing Committee and other relevant inputs, the Government finalized the LLP Bill, 2008. On 21st October, 2008, the revised Bill was again introduced in Rajya Sabha and it finally got passed on 24th October 2008. Later, the Bill was passed by Lok Sabha on 12th December, 2008, and received President’s assent on 7th January 2009, and thus Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 came into force.
The main provisions or the highlights of the Act are as follows:
- Any two or more persons,by subscribing there names to the incorporating document and after filing it with Registrar can form a LLP.
- The LLP shall be a body corporate and shall have a separate entity different from its members.
- The LLP shall have a perpetual succession means that the corporation or organization would continue to exist despite of death, bankruptcy, insanity, change in membership or an exit of a partner.
- While the LLP has a separate legal entity, liable to the full extent of its assets, the liability of the partners would be limited to their agreed contribution in the LLP. No partner would be liable on account of the independent or unauthorized actions of other partners, thus allowing individual partners to be shielded from joint liability created by another partner’s wrongful business decisions or misconduct.
- Indian Partnership Act,1932 shall not be applicable to the LLP and unlike traditional partnerships where maximum number of partners cannot exceed 20, there shall be no such upper limit in case of LLP.
- Every LLP shall have at least two partners and shall also have at least two individuals as Designated Partners, of whom at least one shall be resident in India. The duties and obligations of Designated Partners shall be as provided in the law.
- The mutual rights and duties of partners of an LLP inter se and those of the LLP and its partners shall be governed by an agreement between partners or between the LLP and the partners subject to the provisions of the LLP Act 2008. The act provides flexibility to devise the agreement as per their choice. In the absence of any such agreement, the mutual rights and duties shall be governed by the provisions of Schedule I of LLP Act.
- An audited Annual Accounts are required to be maintained by every LLP reflecting a true n fair view of its state of affairs. In addition to this a statement of accounts and solvency shall also be filed by every LLP with the Registrar every year.
- The Central Government has powers to investigate the affairs of an LLP, if required, by appointment of competent Inspector for the purpose.
- A firm, private company or an unlisted public company is allowed to be converted into LLP in accordance with the provisions of the Act. Upon such conversion, on and from the date of certificate of registration issued by the Registrar in this regard, the effects of the conversion shall be such as are specified in the LLP Act.
- The winding up of the LLP may be either voluntary or by the Tribunal to be established under the Companies Act, 1956. Till the Tribunal is established, the power in this regard has been given to the High Court.
- The law would confer powers on the Central Government to apply such provisions of the Companies Act, 1956 to provide, inter-alia, for mergers, amalgamations, winding up and dissolution of LLPs, as appropriate, by notification with such changes or modifications as deemed necessary. However, such notifications shall be laid in draft before each House of Parliament for a total period of 30 days and shall be subject to any modification as may be approved by both Houses.
BRIEF PROCESS OF INCORPORATING A LLP IN INDIA
- Minimum two of the partners have to obtain a Designated Partner Identification Number by applying in Form 7 on the LLP website. A physical set of documents along with valid proof are sent to the Department for validation.
- Name Availability Form 1 has to be filed by two designated partners.
- Once name availability is confirmed then, Incorporation Form 2 has to be filed stating the details of the partners. A proof of the registered office has to be attached with the form.
- Information with regard to LLP Agreement has to be filed with in one month of Incorporation in Form 3
- Consent of partner to become a partner/designated partner has to be filed in Form 4 within one month of incorporation.
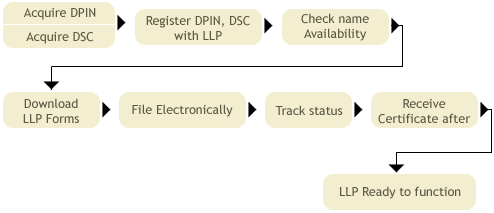
** this picture is an extract from the LLP website (http://www.llp.gov.in/)
RESPONSE TOWARDS LLPs BY THE INDIAN MARKET:
The rules in respect of registration and operational aspects under the LLP Act, 2008 viz. LLP Rules, 2009, were issued on 1st April, 2009. The rules in respect of conversion of a partnership firm, a private company and an unlisted public company into LLPs were made effective w.e.f. 31st May, 2009. The Government also launched a website namely www.llp.gov.in on 1st April,2009 for registration and governance of LLPs.
This introduction of LLPs in Indian Market was taken hand to hand and consequently a bullish response was seen. The first LLP got registered on 2nd April,2009,the very next day of the issue of rules regarding LLPs and as by the current data , till 5th October 2009,the registered number of LLPs has increased up to 248.
TAXATION ISSUES:
The Union Budget 2009 announced on July 6, 2009 the road map for the taxation of the LLPs in India. The new provisions introduced in relation to the taxation of LLP do not treat the LLP as a transparent entity but treat the same at par with the general partnerships under the Indian Partnership Act, 1932. Accordingly, the profits and losses of the LLP would not pass
through in the hands of the partners but would be assessable in the hands of the LLP. The definition of “firm”, “partner” and “partnership” under section 2(23) of the Income Tax Act, 1961 (‘IT Act’) have also been extended to include LLP, a partner in a LLP and LLP respectively within their scope. Accordingly, all the provisions relating to the partnership firm apply mutatis mutandis to LLPs.
LLPs have also been excluded from the provisions of section of 44AD of the Income Tax Act, which provide for an option of the income of the general partnerships to be taxed at a presumptive rate of 8%. A new section 167C has been introduced in the IT Act, which makes every partner of a LLP jointly and severally liable for the taxes to be paid by the LLP for the period during which he is a partner, unless the non-recovery of taxes cannot be attributed to gross neglect, misfeasance or breach of duty on his part.
Some of the key highlights of tax on LLPs are as follows:
- LLPs will be treated as Partnership Firms for the purpose of Income Tax w.e.f. assessment year 2010-11 .
- No surcharge will be levied on income tax.
- Profit will be taxed in the hands of the LLP and not in the hands of the partners.
- Minimum Alternate Tax and Dividend Distribution Tax will not be applicable for LLP.
- Remuneration to partners will be taxed as “Income from Business & Profession”.
- No capital gain on conversion of partnership firms into LLP.
- Designated Partners will be liable to sign and file the Income Tax return.
Thus all the aforesaid factors make LLP an attractive mode of business so far as the tax cost is concerned.
GLOBAL COMPARISON:
Comparison of legal regime of Indian LLP with United States and United Kingdom LLP:
| S. No | Particulars | United States LLP | Indian LLP | United Kingdom LLP |
| 1. | Registration with required authority |
Registration with Secretary of the States. |
Registration with Registrar of Companies required. |
Registration with Companies House required. |
| 2 | Document of Registration |
Form LLP-1 |
LLP Agreement |
LLP Agreement |
| 3. | Distinct entity |
Is a separate legal entity under the Uniform Partnership Act ,1996. Each Individual States have passed Revised Uniform Partnership Act 1997 to implement LLP in their own states. It means LLP legislation in one specific states is different from other |
Is a separate legal entity under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 |
Separate legal entity under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2000, operating under a combination of partnership and company law. |
| 4. | Name of Entity |
Name to contain ‘Limited Liability Partnership’ or ‘LLP’ /RLLP as suffix |
Name to contain ‘Limited Liability Partnership’ or ‘LLP’ as suffix |
Name to contain ‘Limited Liability Partnership’ or ‘LLP’ as suffix |
| 5. | Foreign Partnership |
Foreign Nationals can be a Partner in a LLP. Atleast one of the designated partner should be resident in India |
Foreign Nationals can be a Partner in a LLP. |
Foreign Nationals of any nationality can be a Partner in a LLP, further all the partners may be foreign nationals |
| 6. | Liability of Partners/Members |
Limited to the extent of their contribution towards LLP. In case of fraud or omission LLP is liable for partners wrongful act |
Limited to the extent of their contribution towards LLP, except in case of intentional fraud or wrongful act of omission or commission by the partner |
Limited, to the extent of their contribution towards LLP |
| 7. | Maintenance of Statutory Records |
Required to maintain books of accounts |
Required to maintain books of accounts |
Required to maintain books of accounts |
| 8. | Annual Filing |
Annual Return must be filled with the Secretary of States |
Annual Financial Statement and statement of Solvency is required to be filed with Registrar of Companies every year. |
Annual return to be submitted to the Registrar of Companies every year |
| 9. | Borrowing by LLP |
Borrowing Resolution is passed by the partners to take a decision |
As per LLP Agreement |
LLP can borrow money in its own name |
| 10. | Winding Up |
By filing Form LLP-4 with the Secretary of States |
Voluntary or by order of National Company Law Tribunal. |
As per Regulations by applying or incorporating, with or without modifications provisions of Insolvency Acts. |
CONCLUSION:
LLPs have been in rising trend in various other countries such as UK, USA, Australia, Singapore, China, Japan, Germany etc. In this form of business entity, the individual partners are relieved from joint liability of partners in a partnership firm and there liability does not extend to their personal assets. Indian service industry is expanding its horizons, there are a large number of Indian professionals exporting services all over the world. The recognition of LLPs will make them more competitive in International world, and augment the growth of service industry in India. Professionals like Company Secretaries, Chartered Accountants, Cost Accountants, Advocates and others may form multi-disciplinary LLPs to meet the limit their liabilities and grow in the changing economic environment. This hybrid structure of LLP facilitates entrepreneurs, service providers and professionals to constitute, organize and operate in a most efficient and effective manner so as to face the competition in the global market. Indeed the LLP structure will sooner become the most common form of organisation among professionals, and contribute to Corporate World at large.

4 replies on “Limited Liability Partnerships”
Hello there, You have performed a great job. I’ll certainly digg it and for my part recommend to my friends. I am sure they will be benefited from this site.
Hiya very cool website!! Man .. Beautiful .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds additionally?I am happy to seek out numerous useful info right here within the submit, we need work out more techniques on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
I just couldn’t leave your site before suggesting that I really loved the standard info a person provide on your guests? Is gonna be back continuously in order to investigate cross-check new posts
Thank you for some other informative site. The place else could I am getting that kind of info written in such a perfect means? I have a venture that I’m simply now operating on, and I have been on the look out for such info.